2025.12.08~2025.12.14
CNS刊登文章
01
Nature
本周无
02
Science
2025/12/11
1.“Structure and organization of AMPA receptor-TARP complexes in the mammalian cerebellum”
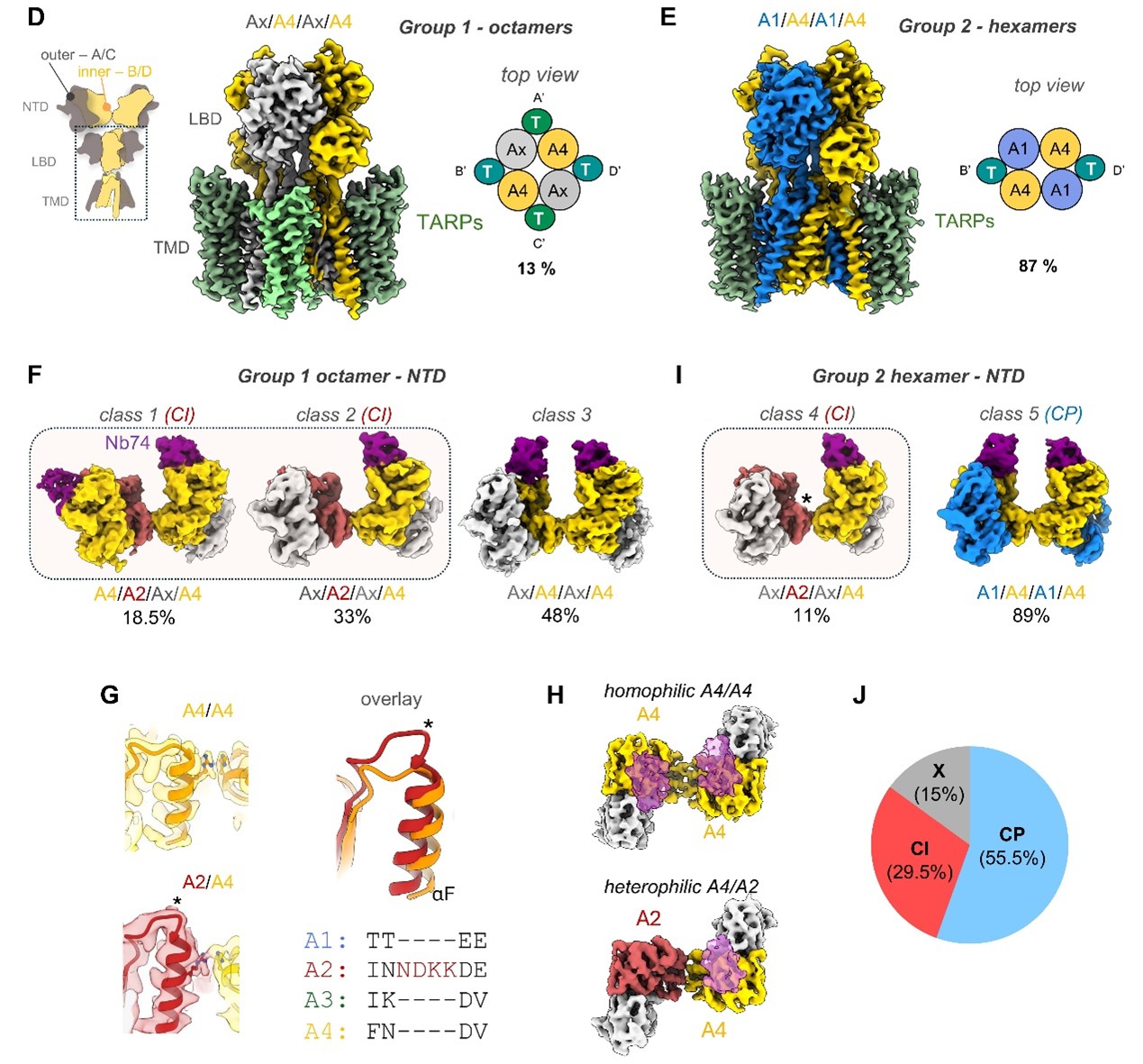
AMPA 受体(AMPAR)是全脑范围内谷氨酸能信号的多模态转导器。它们的多样性在小脑中表现得尤为突出:在传入突触中,AMPAR 介导高频兴奋性传递;而在伯格曼胶质细胞(Bergmann glia,BG)中,AMPAR 则支持钙瞬变,从而调节突触传递。这种功能谱系源于核心亚基(GluA1–4)、辅助蛋白以及转录后修饰的不同组合。
来自MRC分子生物学实验室Ingo H. Greger课题组结合质谱分析、冷冻电镜和电生理手段,对猪小脑中主要的 AMPAR 进行了系统表征。结果发现:一类主要来源于神经元的 AMPAR 为钙不可通透的 GluA2/A4 异源四聚体,并结合四个 TARP 辅助亚基;另一类则为伯格曼胶质细胞特异的钙可通透 GluA1/A4 异源四聚体,仅包含两个 II 型 TARP。研究者还发现,GluA4 受体始终表现出更为紧凑的 N 端结构域,这一特性有利于其突触定位和递送。本研究阐明了哺乳动物小脑 AMPAR 复合物的组织原理,并揭示了不同受体亚型如何支持细胞类型特异性的功能。
03
Cell
2025/12/08
“Structural basis of microtubule-mediated signal transduction”
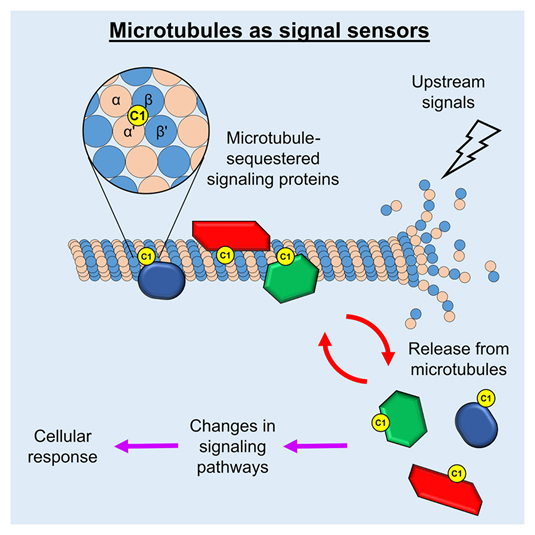
微管长期以来被认为是细胞内信号传导的上游调控因子,但其发挥这一基本功能的分子机制仍不清楚。
来自瑞士保罗谢勒研究所(PSI)生命科学中心的Michel O. Steinmetz课题组揭示了微管调控鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子 H1(GEFH1)的结构基础。GEFH1 是 Ras 同源家族成员 A(RhoA)通路的关键激活因子。研究者发现,微管晶格的特定结构特征能够结合 GEFH1 的 C1 结构域,从而将该信号蛋白隔离并使其失活。针对 C1 结构域关键残基的定点突变会破坏这种相互作用,导致 GEFH1 从微管上释放,并激活 RhoA 依赖的免疫反应。在这一“隔离—释放”调控机制的基础上,研究者进一步鉴定了其他信号蛋白中具有微管结合能力的 C1 结构域,包括其他鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子(GEFs)、激酶、一个 GTP 酶激活蛋白(GAP)以及一种抑癌蛋白,并证明这种通过 C1 结构域介导的微管调控在含 Ras 关联结构域蛋白 1A(RASSF1A)中同样是保守的。本研究建立了一个结构层面的框架,用于理解微管如何作为时空信号传感器,整合并处理多种信号通路,从而调控重要的细胞过程。
2025.12.08~2025.12.14
子刊刊登文章
01
Cell Research
本周无
02
Molecular Cell
12.09
03
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
12.09
1.“EMProt improves structure determination from cryo-EM maps”
12.09
04
Nature Communications
12.08
12.08
2.“Structural and catalytic diversity of coronavirus proofreading exoribonuclease”
12.08
3.“Structure, function, and implications of fucosyltransferases in health and disease”
12.09
12.09
5.“Structural insights into kainate receptor desensitization”
12.09
12.09
7.“Distinct structural features of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATP synthase revealed by cryo-electron microscopy”
12.10
8.“De novo design of epitope-specific antibodies via a structure-driven computational workflow”
12.10
9.“Molecular architecture of the human TRPC1/C5 heteromeric channel”
12.10
12.10
11.“Unveiling cytochrome P450 enzymes that catalyze steroid side-chain cleavage in bacteria”
12.10
12.10
13.“Structural basis of calcium-dependent C1ql1/BAI3 assemblies in synaptic connectivity”
12.11
14.“Structural basis of PANX1 permeation and positive modulation by mefloquine”
12.11
15.“The molecular mechanism of fluoride export by the eukaryotic fluoride channel FEX”
12.11
12.11
17.“Ran modulates allosteric crosstalk between importin β surfaces”
12.11
18.“Structural snapshots of the mechanism of ATP-dependent DNA damage recognition by UvrA”
12.11
12.11
12.11
12.11
22.“Structure of Trypanosoma peroxisomal import complex unveils conformational heterogeneity”
12.12
23.“Mechanisms of light harvesting complex proteins in photoprotection of the brown tide alga”
12.12
12.12
25.“Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of ammonia monooxygenase”
12.12
26.“Structural insights into GM4951 as a lipid droplet GTPase regulating hepatic lipid metabolism”
12.12
27.“Assembly and lipid-gating of LRRC8A:D volume-regulated anion channels”
12.12
12.13
29.“Dynamic nanoscale architecture of synaptic vesicle fusion in mouse hippocampal neurons”
12.13
12.13
31.“Structural basis of double-stranded RNA recognition by the J2 monoclonal antibody”
12.14
12.14
33.“Structural basis for pharmacotherapeutic action of triple reuptake inhibitors”
12.14
34.“Structural characterisation of the fungal Pmt4 homodimer”
12.14
35.“Visualizing insecticide control of insect TRP channel function and assembly”
05
Science Advances
12.10